The brain is divided into main functional sections, called lobes. These sections or brain lobes are called the Frontal Lobe, Temporal Lobe, Parietal Lobe, Occipital Lobe, the Cerebellum, and the Brain Stem. Each has a specific function as described below.
Frontal Lobe Functions
- Attention and concentration
- Self-monitoring
- Organization
- Speaking (expressive language) • Motor planning and initiation
- Awareness of abilities and limitations
- Personality
- Mental flexibility
- Inhibition of behavior
- Emotions
- Problem solving
- Planning and anticipation
- Judgment
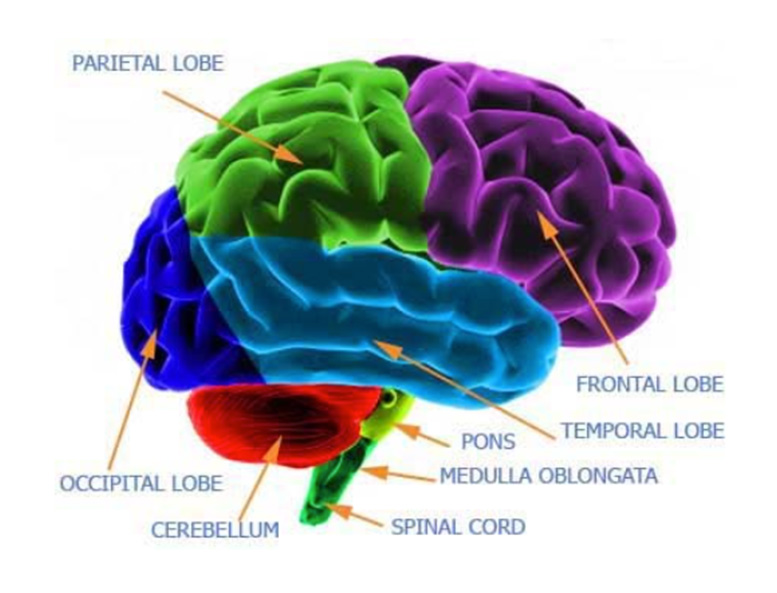
Parietal Lobe
- Sense of touch
- Spatial perception
- Differentiation (identification) of size, shapes, and colors
- Visual perception
Brain Stem
- Breathing
- Arousal and consciousness
- Attention and concentration
- Heart rate
- Sleep and wake cycles
Temporal Lobe
- Memory
- Understanding language (receptive language)
- Sequencing
- Hearing
- Organization
Cerebellum Lobe
- Balance
- Skilled motor activity
- Coordination
Occipital Lobe
- Vision
Right or Left Brain
The functional sections or lobes of the brain are also divided into right and left sides. The right side and the left side of the brain are responsible for different but specific functions. General patterns of dysfunction can occur if an injury is on the right side, left side, or diffused (scattered across both sides). Understanding the associated issues with these particular situations can help caretakers or healthcare providers better understand the needs of an individual.

Injuries of the Left Side of the Brain can cause:
- Difficulties in understanding language (receptive language)
- Difficulties in speaking or verbal output (expressive language)
- Catastrophic reactions (depression, anxiety)
- Verbal memory deficits
- Impaired logic
- Sequencing difficulties
- Decreased control over right-sided body movements
Injuries of the Right Side of the Brain can cause:
- Visual-spatial impairment
- Visual memory deficits
- Left neglect (inattention to the left side of the body)
- Decreased awareness of deficits
- Altered creativity and music perception
- Loss of “the big picture” type of thinking
- Decreased control over left-sided body movements
Diffused Brain Injury can cause:
- Reduced thinking speed
- Confusion
- Reduced attention and concentration
- Fatigue
- Impaired cognitive (thinking) skills in all areas




